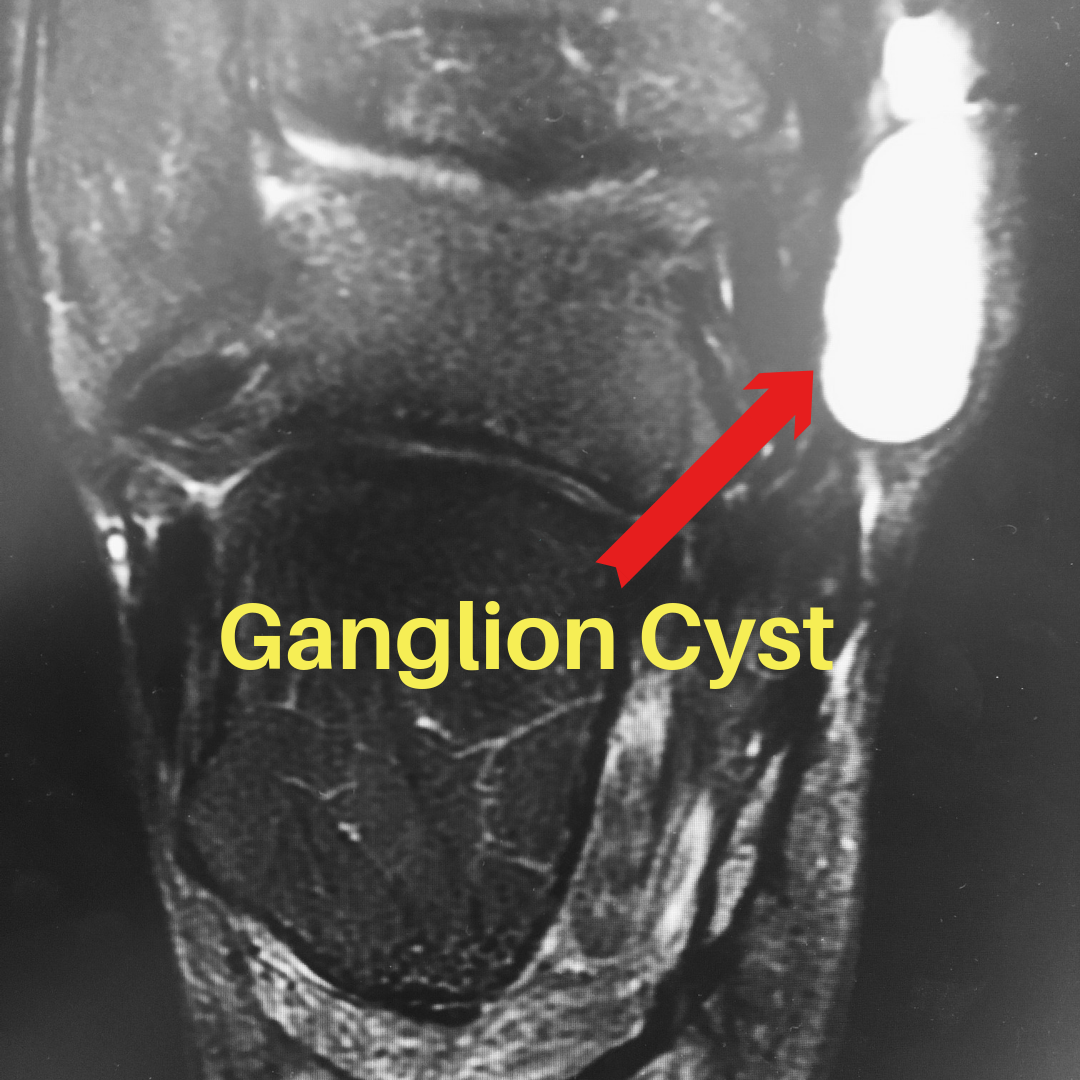
What is a Ganglion Cyst of the Ankle and Foot?
February 12, 2019
Ingrown Toenail
February 12, 2019What is Pediatric Flatfoot?
Pediatric flatfoot is a condition that occurs when there is partial or complete collapse of the foot. Patients can have structural weaknesses at the foot, ankle, and hip. Patients may or may not complain about pain. Parents might notice their children walking and running differently than their peers. Even in the absence of pain, parents should have their child’s feet evaluated if they suspect a flatfoot deformity.
How to Diagnose Pediatric Flatfoot
It’s best to recognize a pediatric flatfoot at an early age. At age 5, a normal arch should be recognizable. The earlier a flatfoot can be managed, the better the long term outcome. Recognition starts with parents. Key factors to recognize:
- Your child has difficulty running, or is unable to keep up in sports.
- Your child frequently complains about foot pain.
- When examining your child’s feet from behind, their heel bones tend to tilt outwards, while their ankles tilt inwards
- You will see a decrease in the arch height.
- Your child’s shoes wear down quickly on the inside of the heel.
How to Treat Pediatric Flatfoot
If you suspect that your child has a flatfoot deformity, schedule an initial consult as soon as possible! Pediatric foot pain and flatfeet can be managed with a medical grade or custom orthotic. Orthotics will align the foot and support the fallen arch. Lower extremity strengthening, as well as glute strengthening is paramount for managing pediatric foot pain and flatfoot deformities.
Minimally invasive surgical options are recommended for older pediatric patients if their flatfoot deformity has failed conservative intervention. Reconstructive flatfoot surgery may also be necessary. Reconstructive surgery is reserved for severe cases that have failed all conservative care.



