How To Run a Fast Revel Big Cottonwood Half Marathon
September 8, 2018
Pediatric Flatfoot
February 12, 2019What Causes a Ganglion Cyst?
A ganglion cyst is a benign lesion that can develop in the ankle or foot. These cysts can vary in size, as well as location. They appear as raised bumps under the skin.
The exact cause of a ganglion cyst is not completely know. Generally the cysts arise from a torn tendon sheath or joint capsule. These injuries can occur with repetitive trauma.
Symptoms of a Ganglion Cyst
A ganglion cyst may or may not be painful. A patient will notice a new lump on their foot. Pressure from certain shoes might cause pain.
Diagnosing Ganglion Cysts
A ganglion cyst will appear as a raised bump under the skin. Sometimes the cyst will transilluminate with light. The ganglion cyst may be painful on clinical exam. It will also be freely mobile under the skin.
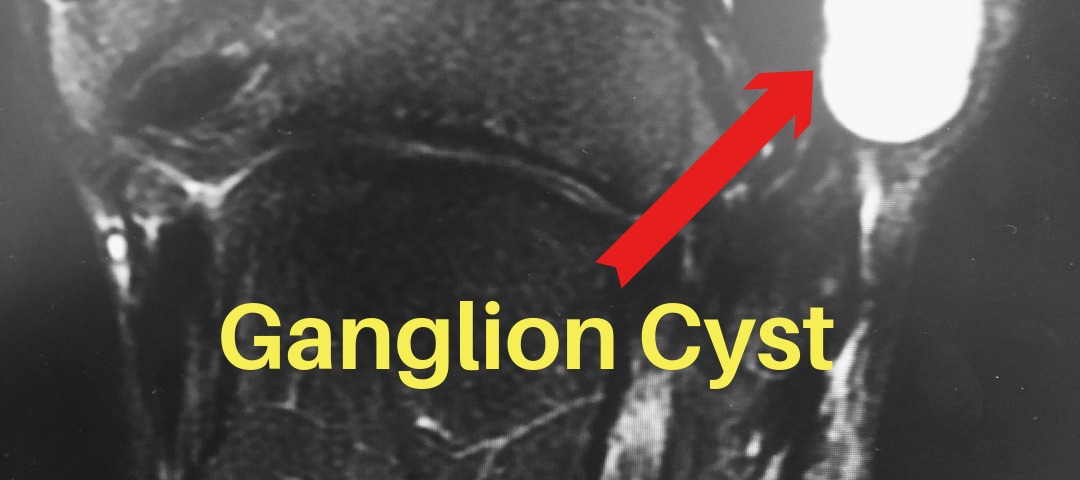
An MRI is the best imaging tool to evaluate the the size and location of the ganglion cyst. Often times, the ganglion cyst infiltrate areas that can not be seen clinically. MRIs are helpful for surgical planning.
Ultrasound can also be used to diagnose a ganglion cyst. An ultrasound evaluation is performed prior to aspiration. The ultrasound will confirm that the mass being evaluated is cystic rather than fibrotic. A cystic mass will aspirate, whereas a fibrotic mass will have to be removed surgically.
Treatment Ganglion Cysts
A ganglion cyst can be treated both conservatively as well as surgically.
Conservative treatment includes doing nothing to treat the cyst. A lot of patients just want the confirmation that they mass growing on their ankle or foot is benign. If the cyst does not cause pain, most patients elect not to have it removed.
A ganglion cyst can also be aspirated (i.e drained) in clinic. The procedure involves a sterile prep, a small amount of local anesthetic injected in the superficial skin layer, and a needle to puncture the cyst. Once the local anesthetic is administered, the procedure is painless. A small needle is punctured through the cyst a few times to allow all the fluid to drain out. This should take several minutes to insure that all the fluid was aspirated. A sterile dressing is then placed over the procedure site, and patients can remove it the following day to shower.
Surgical excision of the cyst is an outpatient procedure. In an operating room, under anesthesia, a small incision is made over the cyst, and the cyst is carefully removed. The cyst is encapsulated by a very thin sac and a stalk is connected to the corresponding damaged joint capsule or tendon sheath. It is important to find the origin of the stalk and remove the entire cyst from this point. The cyst should be sent to pathology to confirm that it is a benign ganglion cyst.
Surgery is always an outpatient procedure. Patient walk out of surgery the same day. Sutures are removed around 10-14 days post op. Patients have no activity restrictions after suture removal.
Can Ganglion Cysts Reoccur?
It is not uncommon for ganglion cysts to reoccur after an aspiration procedure. Sometimes surgical excision is necessary to remove the sac that encapsulates the cyst. Most patients prefer to have a couple of aspiration attempts prior to moving forward with surgery.